Navigating the intricate social landscape is a fundamental aspect of life, especially during formative years. For many individuals, particularly those with diverse needs, cultivating effective social skills can be a challenging journey. Positive Behaviour Support (PBS) emerges as a transformative approach, not only addressing individual behaviours but also fostering positive peer relationships. In this blog post, we will explore the profound impact of PBS on cultivating social skills and building meaningful connections among peers.
Understanding the Role of Social Skills: A Crucial Aspect of Development

Social skills encompass a broad range of abilities that facilitate effective interactions and relationships with others. These skills include communication, empathy, cooperation, problem-solving, and self-regulation – all essential for building positive peer relationships. For individuals facing challenges in these areas, the journey toward developing strong social skills is pivotal for overall well-being and successful social integration.
Positive Behaviour Support: A Holistic Approach to Social Skill Development
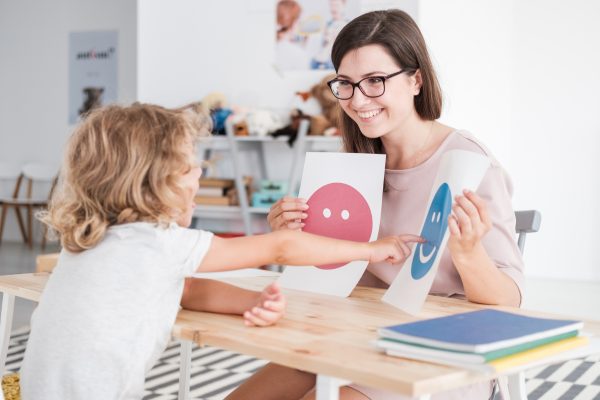

Positive Behaviour Support transcends traditional behaviour management methods by adopting a holistic and proactive approach. Instead of focusing solely on addressing challenging behaviours, PBS emphasizes creating environments that encourage positive behaviours and explicitly teaching the skills needed for successful social interactions. The application of PBS in cultivating social skills is multifaceted, incorporating various strategies to promote a positive and inclusive social environment.
1. Social Stories and Visual Supports:
Social stories are narrative interventions that provide individuals with information about social situations, expected behaviours, and appropriate responses. In the context of PBS, social stories can be tailored to address specific social scenarios or challenges, offering guidance and promoting understanding. Visual supports, such as visual schedules and cues, complement social stories by providing clear visual guidance during social interactions.
2. Peer-Mediated Interventions
Peer-mediated interventions involve actively engaging peers to support and reinforce positive social behaviours. By fostering an inclusive environment and educating peers about diverse needs, PBS promotes collaboration and understanding. Peers can serve as role models, providing guidance and positive reinforcement, contributing to the development of social skills among all individuals.
3. Teaching Communication Skills
Effective communication is a cornerstone of successful social interactions. PBS places a strong emphasis on explicitly teaching communication skills, including verbal and nonverbal communication. Individuals learn to express themselves clearly, understand others’ perspectives, and navigate social nuances. Communication skills are essential for building connections and establishing positive peer relationships.
4. Role-Playing and Social Scripts
Role-playing and social scripts are interactive strategies used in PBS to provide individuals with opportunities to practice and reinforce social skills in a controlled setting. By simulating social scenarios, individuals can experiment with different responses, receive feedback, and gain confidence in applying social skills in real-life situations.
5. Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a foundational concept in PBS and is equally powerful in social skill development. By recognizing and reinforcing positive social behaviours, individuals are motivated to continue engaging in prosocial actions. This positive feedback loop strengthens the connection between positive behaviours and the rewards of successful social interactions.
6. Structured Social Activities
Structured social activities provide a supportive framework for practicing and developing social skills. PBS encourages the creation of structured and predictable social opportunities, such as group activities, games, or collaborative projects. These activities offer a controlled environment for individuals to practice social skills while enjoying positive peer interactions.
7. Building Empathy and Perspective-Taking
Empathy and perspective-taking are integral components of social skills. PBS incorporates activities and discussions that promote understanding of others’ feelings and perspectives. By fostering empathy, individuals develop a deeper appreciation for diversity, enhance their social awareness, and contribute to a more compassionate and inclusive social environment.
8. Social Reinforcers
In addition to traditional reinforcers, social reinforcers play a significant role in PBS. These include verbal praise, acknowledgment, and social approval. Social reinforcers are particularly potent in the context of peer relationships, as positive feedback from peers serves as a motivating factor for individuals to continue practicing and refining their social skills.
9. Individualized Social Goals
Recognizing the uniqueness of individuals, PBS encourages the development of individualized social goals. These goals are tailored to address specific social challenges or target areas for improvement. Individualization ensures that interventions are meaningful and aligned with the individual’s unique strengths and needs.
10. Collaborative Problem-Solving
Collaborative problem-solving is a central tenet of PBS that extends to social skill development. Instead of imposing solutions, PBS involves individuals in identifying social challenges, brainstorming strategies, and collaboratively developing solutions. This inclusive approach empowers individuals, promoting a sense of ownership and active participation in their social development.
Case Study: Nurturing Social Skills Through Positive Behaviour Support
Ryan, a middle school student with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), experiences challenges in social situations. He often interrupts conversations, struggles with turn-taking, and has difficulty maintaining friendships due to impulsive behaviours.
Positive Behaviour Support Approach:

1. Functional Behaviour Assessment (FBA):
Conduct a Functional Behaviour Assessment to understand the antecedents and triggers of Ryan’s social challenges. The analysis reveals that difficulties in impulse control and challenges in understanding social cues contribute to his behaviours.
2. Social Stories and Visual Supports
Develop social stories and visual supports to address specific social scenarios that pose challenges for Ryan. These tools provide clear guidance on expected behaviours, appropriate responses, and visual cues to support understanding during social interactions.
3. Peer-Mediated Interventions
Implement peer-mediated interventions by educating Ryan’s peers about ADHD, its impact on social interactions, and strategies to support him. Assign peers as social buddies to provide guidance and positive reinforcement, fostering an inclusive and supportive peer environment.
4. Teaching Communication Skills
Explicitly teach communication skills to Ryan, focusing on turn-taking, active listening, and nonverbal cues. Engage in role-playing activities to provide practical opportunities for him to practice and reinforce these skills in a controlled setting.
5. Positive Reinforcement
Implement a positive reinforcement system that recognizes and reinforces Ryan’s positive social behaviours. Verbal praise, social approval, and acknowledgment from peers serve as powerful reinforcers, motivating him to continue engaging in socially appropriate actions.
6. Structured Social Activities
Create structured social activities that provide a supportive framework for Ryan to practice and develop social skills. These activities include group projects, collaborative games, and structured discussions that promote positive peer interactions and the application of learned social skills.
7. Building Empathy and Perspective-Taking
Integrate activities and discussions that enhance Ryan’s empathy and perspective-taking abilities. Engage him in conversations about others’ feelings, experiences, and perspectives, fostering a deeper understanding of social dynamics and promoting empathy in social interactions.
8. Social Reinforcers
Emphasize social reinforcers by highlighting the positive social consequences of appropriate behaviours. Encourage peers to provide positive feedback and acknowledgment when Ryan demonstrates improved social skills, reinforcing the connection between positive behaviours and social approval.
9. Individualized Social Goals
Develop individualized social goals for Ryan based on his unique challenges and strengths. These goals address specific areas for improvement, such as reducing interruptions, improving turn-taking, and enhancing overall social awareness.
Transform Life is a NDIS registered organisation that provides support for your autistic child, as well as support to you as a parent to best navigate the challenges your child and family face on a daily basis.
Book your consult with an experienced Therapist at Transform Life to explore how Positive Behaviour Support can support you and your family.